
Quantum Efficiency Tester
PL/EL Integrated System
PV-Reflectumeter
3D Confocal Microscope
In-Line Four Point Probe Tester
Four Point Probe Tester
In-Line Thin Film Thickness Tester
Raman Spectrometer
FTIR Spectrometer
Spectrophotometer
Automatic Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
Contact Resistance Tester
Ultra depth of field 3D microscope
Auto Visual Tester
VMM PV Vision Measuring Machine
Solar Cell Horizontal Tensile Tester
Steady State Solar Simulator for Solar Cell
Solar Cell UV Aging Test Chamber
Solar Cell Comprehensive Tensile Tester
Visual Inspection Tester
Wet Leakage Current Tester
PV Module EL Tester
PV Module UV Preconditioning Chamber
Steady State Solar Simulator for PV Module
Current Continuous Monitor
Potential Induced Degradation Test
Bypass Diode Tester
LeTID Test System
Reverse Current Overload Tester
Impulse Voltage Tester
Hipot Insulation Tester
Ground Continuity Tester
Hipot Insulation Ground Tester
Damp Heat Test Chamber
Humidity Freeze Test
Thermal Cycle Test Chamber
Dynamic Mechanical Load Tester
Static Mechanical Load Tester
Hail Impact Tester
Robustness of Termination Tester
Module Breakage Tester
Cut Susceptibility Tester
Peel Shear Strength Tester
Universal Testing Machine (Single-arm)
Universal Testing Machine (Double-arm)
Glass Transmittance Tester
Acetic Acid Test Chamber
EVA Degree of Crosslinking Test System
Junction Box Comprehensive Tester
Drop ball tester
Semi-automatic scanning four-probe tester
Stylus Profilometer
Maximum Power Point Tracker
Perovskite Glass Transmittance Tester
Perovskite P1 Laser Scribing Multifunctional Testing Machine
Perovskite Online PL Tester
Perovskite Online Sheet Resistance Tester
Online Perovskite Film Thickness Tester
Perovskite Process Inspection Workstation
Portable IV Curve Tester
Portable EL Tester
Portable Thermal Imaging Tester
Solar Module Multi-Channel Testing System
PV Inverter Power Quality Tester
Drone EL Tester
IV Tester
IVEL Cell Sorting Machine
Enhancing Environmental Stability and Efficiency of Perovskite Solar Cells: A Strategy Based on Sb³⁺/S²⁻ Alloyed FAPbI₃
Date : 6 February 2026Views : 50
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have garnered significant attention due to their exceptional photovoltaic conversion efficiency. However, most high-efficiency PSCs still require fabrication under inert atmospheres (e.g., nitrogen-filled glove boxes), which to some extent limits their large-scale commercial production. Developing highly efficient and stable PSCs under ambient conditions via a two-step process is crucial for advancing their industrial application. The Millennial Temperature and Humidity Combined Environmental Test Chamber is specifically designed to validate and evaluate the reliability of modules or materials. It achieves rapid temperature cycling, enhances testing efficiency, and complies with standards such as IEC 61215.
This paper proposes a novel component engineering strategy. Through a sequential process in ambient air, trivalent antimony (Sb³⁺) and divalent sulfur (S²⁻) ions are simultaneously alloyed into the lead formamide iodide (FAPbI₃) lattice. This significantly enhances the material's intrinsic stability and battery performance.
Research Methods and Material Preparation
Perovskite films were prepared under ambient air conditions using a sequential deposition method. First, a solution of SbCl₃-thiourea (Sb-TU) complex was spin-coated onto a PbI₂ substrate at 150°C. Subsequently, a solution of formamidine iodide (FAI) was introduced to complete the conversion reaction, forming FAPbI₃ films with Sb³⁺/S²⁻ alloying. By systematically varying the Sb-TU loading (0–2.0 mol%), the crystal structure and optoelectronic properties of the material were optimized.
Alloying Effect and Mechanism Analysis
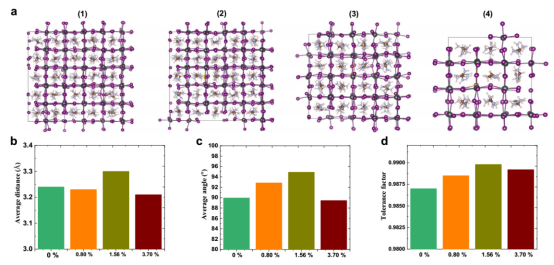
First-Principles Molecular Dynamics (AIMD) Simulations of Sb³⁺/S²⁻ Alloying in FAPbI₃
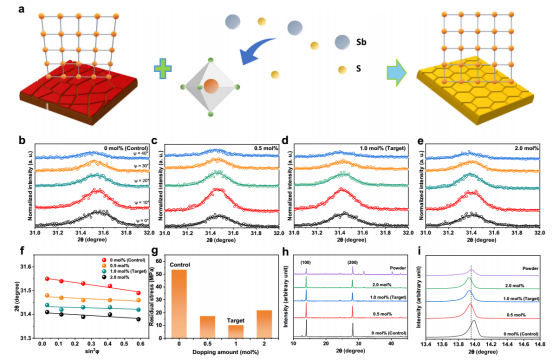
Effects of Sb³⁺ and S²⁻ Doping on Residual Stress and Crystal Structure in Perovskite Thin Films
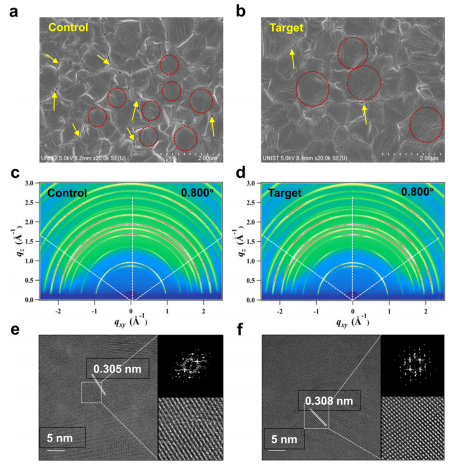
Morphology and Crystallinity Comparison
Theoretical simulations and experimental characterization jointly reveal the multiple benefits of Sb/S alloying:
Lattice Strain Relaxation: Ab initio molecular dynamics simulations indicate that moderate Sb³⁺/S²⁻ doping (~1.56 mol%) modulates Pb–I bond lengths and I–Pb–I bond angles, enhancing the tolerance factor to effectively release lattice stress.
Reduced Residual Stress: Grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction (GIXRD) analysis shows that 1.0 mol% alloyed films exhibit the lowest residual stress (10.5 MPa), less than one-fifth of the control sample (53.7 MPa).
Optimized crystallinity and orientation: GIWAXS and HR-TEM results indicate that Sb³⁺/S²⁻ introduction promotes preferential growth of the α(200) crystal orientation, enhances crystalline quality, and induces more grains to adopt out-of-plane orientation, facilitating charge transport.
Enhanced battery performance and stability
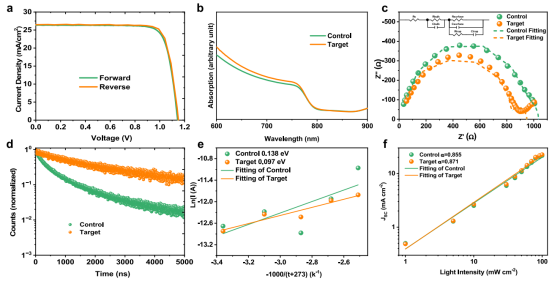
Performance and Characterization Analysis Comparison
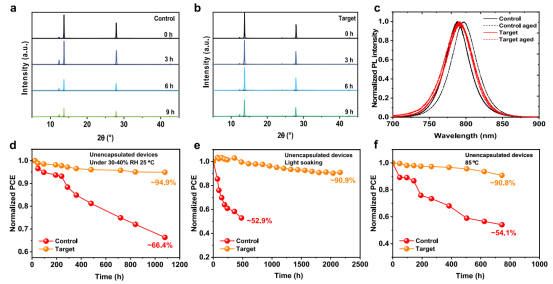
Stability Comparison Analysis of “Control” and “Target” Perovskite Films and Cells
Based on optimized alloyed FAPbI₃, the constructed n-i-p type cell achieved a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 25.07%, with parameters as follows: Jₛc = 26.48 mA/cm², Vₒc = 1.15 V, FF = 82.33%. This efficiency matches the current highest level achievable with atmospheric fabrication processes.
The performance enhancement stems from: increased light absorption and reduced trap density; carrier lifetime extended from 0.82 μs to 2.1 μs; and decreased interface defects suppressing charge recombination.
Regarding stability, the unencapsulated alloyed cell demonstrated outstanding performance: after 1080 hours at 20–40% RH and 25°C in darkness, it retained 94.9% of its initial efficiency; after 2160 hours of continuous illumination at one sun (in an N₂ environment), the efficiency retention exceeded 90%; and after 744 hours at 85°C, the initial PCE was maintained at 90.8%.
This study successfully developed a novel approach to enhance the performance of FAPbI₃ perovskite materials through Sb³⁺/S²⁻ dual-element alloying. This strategy not only significantly enhances cell efficiency and environmental stability but also enables controlled fabrication under ambient atmospheric conditions, overcoming the limitations of traditional inert atmosphere preparation. It holds promising prospects for industrial application. The simultaneous Sb³⁺/S²⁻ alloying approach provides a robust material design concept and technical pathway for developing highly efficient, stable, and scalable perovskite solar cells.
Millennial Temperature and Humidity Combined Environmental Test Chamber

email:market@millennialsolar.com
The Millennial Temperature and Humidity Combined Environmental Test Chamber utilizes an imported temperature controller, enabling multi-stage temperature programming with high precision and excellent reliability to meet testing requirements under various climatic conditions.
▶ Temperature Range: 20°C to +130°C
▶ Temperature and Humidity Range: 10%RH to 98%RH (at +20°C to +85°C)
▶Compliant with Testing Standards: IEC61215, IEC61730, UL1703, and other certification requirements
The Millennial Temperature and Humidity Environmental Test Chamber delivers a comprehensive climate simulation solution for photovoltaic module testing. It precisely accelerates accelerated aging experiments and fully ensures module reliability certification. By leveraging standardized intelligent control to drive industrial advancement, it provides robust support for breakthroughs in highly stable, scalable perovskite modules.
Related Products

































































