
Quantum Efficiency Tester
PL/EL Integrated System
PV-Reflectumeter
3D Confocal Microscope
In-Line Four Point Probe Tester
Four Point Probe Tester
In-Line Thin Film Thickness Tester
Raman Spectrometer
FTIR Spectrometer
Spectrophotometer
Automatic Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
Contact Resistance Tester
Ultra depth of field 3D microscope
Auto Visual Tester
VMM PV Vision Measuring Machine
Solar Cell Horizontal Tensile Tester
Steady State Solar Simulator for Solar Cell
Solar Cell UV Aging Test Chamber
Solar Cell Comprehensive Tensile Tester
Visual Inspection Tester
Wet Leakage Current Tester
PV Module EL Tester
PV Module UV Preconditioning Chamber
Steady State Solar Simulator for PV Module
Current Continuous Monitor
Potential Induced Degradation Test
Bypass Diode Tester
LeTID Test System
Reverse Current Overload Tester
Impulse Voltage Tester
Hipot Insulation Tester
Ground Continuity Tester
Hipot Insulation Ground Tester
Damp Heat Test Chamber
Humidity Freeze Test
Thermal Cycle Test Chamber
Dynamic Mechanical Load Tester
Static Mechanical Load Tester
Hail Impact Tester
Robustness of Termination Tester
Module Breakage Tester
Cut Susceptibility Tester
Peel Shear Strength Tester
Universal Testing Machine (Single-arm)
Universal Testing Machine (Double-arm)
Glass Transmittance Tester
Acetic Acid Test Chamber
EVA Degree of Crosslinking Test System
Junction Box Comprehensive Tester
Drop ball tester
Semi-automatic scanning four-probe tester
Stylus Profilometer
Maximum Power Point Tracker
Perovskite Glass Transmittance Tester
Perovskite P1 Laser Scribing Multifunctional Testing Machine
Perovskite Online PL Tester
Perovskite Online Sheet Resistance Tester
Online Perovskite Film Thickness Tester
Perovskite Process Inspection Workstation
Portable EL Tester
Portable Thermal Imaging Tester
Solar Module Multi-Channel Testing System
PV Inverter Power Quality Tester
Drone EL Tester
IV Tester
IVEL Cell Sorting Machine
Fraunhofer ISE's latest study: Hygrothermal DH and UV-UV attenuation mechanisms in TOPCon PV modules
Date : 25 July 2025Views : 2205
With PV plant lifetimes needing to exceed 20 years, reliability testing and quality assurance are critical, especially with respect to moisture ingress and resistance to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards (e.g. IEC 61215) provide guidelines for indoor accelerated aging tests, but the challenge lies in how to correlate with actual outdoor conditions.TOPCon technology is susceptible to moisture corrosion due to the silver-aluminum (Ag-Al) paste front surface metallization, and the SiNx passivation layer is prone to fracture of the Si-H bond under UV, leading to an increase in defect density. Among them, Millennial temperature and humidity integrated environmental test chamber can carry out indoor accelerated aging to meet the IEC61215 and other standards. In this study, we explore the attenuation mechanism of TOPCon, HJT, and PERC modules through indoor humid-heat DH aging and UV-UV aging combined with subsequent 8-month outdoor exposure.
Experimental Methods
Samples and Grouping
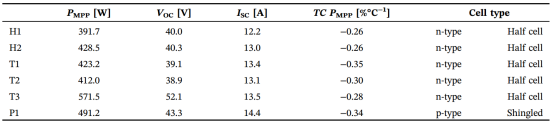
Three common bifacial PV modules on the market were selected: HJT (H1, H2), TOPCon (T1, T2, T3) and PERC (P1). The initial parameters of all samples were measured under laboratory standard test conditions (STC), covering key indicators such as maximum power (PMPP), open-circuit voltage (Voc), and short-circuit current (Isc).
PV module parameters (frontal exposure) and temperature coefficient of maximum power (TC PMPP) measured under laboratory STC
Experimental Design
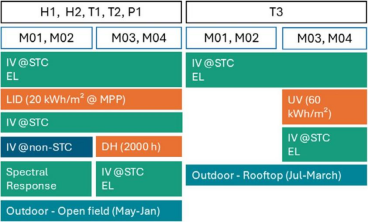
Overview of the experimental procedure: (left) Damp heat aging experiment setup; (right) UV aging experiment setup. Green is standard test conditions (STC), blue is non-STC test, and orange is accelerated aging procedure.
Two sets of aging experiments are conducted, Damp Heat DH and UV UV. Four samples of each type of PV module were taken: two “new” samples (M01, M02) were subjected to STC and non-STC indoor characterization according to IEC 61853-1, and two samples (M03, M04) were subjected to accelerated aging with STC testing before and after aging. All samples were subsequently exposed outdoors for approximately 8 months (beginning of summer), during which time their IV curves were continuously monitored in MPP operation.
Indoor accelerated aging
Damp heat aging group according to IEC 61215-2 standard, test at 85℃, 85% RH condition for 2000 hours; UV aging group adopts the scheme modified from IEC 61730-2, 60 kWh/m² UV dose exposure.
Outdoor exposure

(left) Damp heat test setup in the outdoor performance laboratory of Fraunhofer ISE, Germany; (right) UV aging test setup.
The DH samples were mounted on an open stand (30° inclination) in Merdingen, Germany;
UV samples were placed on the roof of Freiburg (backside masked to simulate a single-sided assembly).
Data processing
Characterization parameters such as Isc, Voc, PMPP, FF and Rs were obtained from IV curves. The data was filtered to an irradiance range of 775-825 W/m² and normalized to 800 W/m² and 42.5°C to reduce measurement uncertainty.
Impact of Damp Heat Aging on Module Performance
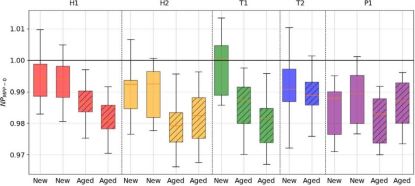
DH aging test module first week outdoor performance (NP_MPP-0), dotted line box diagram for lab aging samples
Indoor DH aging tests show that the performance degradation of different types of modules varies. HJT (H1, H2) and TOPCon (T1) have larger PMPP degradation (2.5%-3%), mainly due to the decrease of FF and the increase of Rs, while the degradation of TOPCon (T2) and PERC (P1) is relatively slight (<2%).
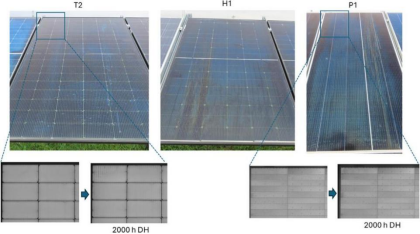
T2, H1, P1 modules DH aging 2000h after 5 months outdoor appearance inspection (visible edge discoloration and drip marks)
Outdoor exposure further reveals the long-term effects of moisture and heat aging: the aging samples of TOPCon (T1) show a continuous degradation of 9.75% in PMPP, a 9.4% decrease in FF, and an increase of about 20% in Rs in 8 months, and the EL image shows a clear dark zone at the edge of the samples, which confirms that corrosion degradation is triggered by the intrusion of moisture; and the performance of HJT (H2) is also declined due to the discoloration of the package and the increase of Rs caused by moisture intrusion. It is worth noting that the degradation of some brand new modules (e.g., H2, P1) after 8 months of outdoor exposure exceeds the indoor test results, suggesting that new degradation mechanisms may be activated by the complex outdoor environment.
Impact of UV Aging on Module Performance
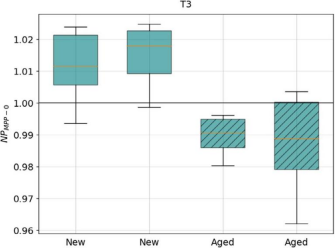
TOPCon-T3 module first week outdoor performance (NPMPP-0), dashed box plot shows UV aged sample
TOPCon (T3) UV aging tests show a 2.5% drop in PMPP and a 1.5% drop in Voc after 60 kWh/m² of UV exposure, which correlates with degradation of the surface passivation layer. At the beginning of outdoor exposure (within 1 week), the difference in PMPP between aged and new samples is 2.4%, which is in line with the indoor results; as the exposure is prolonged, the Voc of the aged samples tends to stabilize under the natural day/night cycle, which confirms the “stabilizing effect” of the UV degradation in outdoor environments.
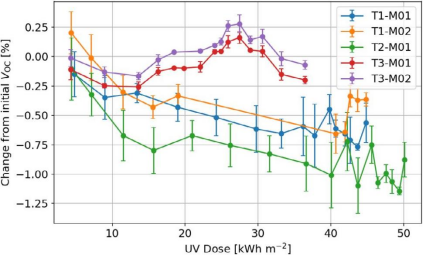
Evolution of Voc for all new TOPCon samples during outdoor exposure (with back masking differences)
In addition, the comparison of TOPCon components with different mounting methods reveals that the Voc degradation of the open bracket-mounted T1 and T2 components (without back shading) is up to 1%, while the Voc degradation of the back-shaded T3 component is less than 0.25%, suggesting that the backside UV radiation may be one of the degradation factors of the outdoor Voc, which needs to be further investigated.
This study proposes a combined indoor-outdoor measurement method for exploring the specific degradation mechanism of TOPCon modules and comparing it with heterojunction (HJT) and passivated emitter back contact (PERC) technologies. Modules were subjected to accelerated moisture-heat DH or UV-UV aging and then co-exposed outdoors with unaged samples. The methodology reveals the severity of moisture ingress and its effect on the increase in series resistance and decrease in fill factor, and identifies the drop in open-circuit voltage (VOC) during UV aging as the main cause of the performance degradation, while validating the stabilization behavior equivalent to day/night cycling in the laboratory.
Millennial Temperature and Humidity Comprehensive Environmental Test Chamber

email:market@millennialsolar.com
Millennial temperature and humidity integrated environmental test chamber adopts imported temperature controller, which can realize multi-stage temperature programming with high accuracy and good reliability to meet the testing needs under different climatic conditions.
Temperature range: 20℃~+130℃
Temperature and humidity range: 10%RH~98%RH(at+20℃-+85℃)
Meet the test standards: IEC61215, IEC61730, UL1703 and other testing standards
Millennial temperature and humidity integrated environmental test chamber can provide reliable indoor accelerated aging test, in line with IEC testing standards, for accurate simulation of hot and humid stress environment.
































































