
Quantum Efficiency Tester
PL/EL Integrated System
PV-Reflectumeter
3D Confocal Microscope
In-Line Four Point Probe Tester
Four Point Probe Tester
In-Line Thin Film Thickness Tester
Raman Spectrometer
FTIR Spectrometer
Spectrophotometer
Automatic Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
Contact Resistance Tester
Ultra depth of field 3D microscope
Auto Visual Tester
VMM PV Vision Measuring Machine
Solar Cell Horizontal Tensile Tester
Steady State Solar Simulator for Solar Cell
Solar Cell UV Aging Test Chamber
Solar Cell Comprehensive Tensile Tester
Visual Inspection Tester
Wet Leakage Current Tester
PV Module EL Tester
PV Module UV Preconditioning Chamber
Steady State Solar Simulator for PV Module
Current Continuous Monitor
Potential Induced Degradation Test
Bypass Diode Tester
LeTID Test System
Reverse Current Overload Tester
Impulse Voltage Tester
Hipot Insulation Tester
Ground Continuity Tester
Hipot Insulation Ground Tester
Damp Heat Test Chamber
Humidity Freeze Test
Thermal Cycle Test Chamber
Dynamic Mechanical Load Tester
Static Mechanical Load Tester
Hail Impact Tester
Robustness of Termination Tester
Module Breakage Tester
Cut Susceptibility Tester
Peel Shear Strength Tester
Universal Testing Machine (Single-arm)
Universal Testing Machine (Double-arm)
Glass Transmittance Tester
Acetic Acid Test Chamber
EVA Degree of Crosslinking Test System
Junction Box Comprehensive Tester
Drop ball tester
Semi-automatic scanning four-probe tester
Stylus Profilometer
Maximum Power Point Tracker
Perovskite Glass Transmittance Tester
Perovskite P1 Laser Scribing Multifunctional Testing Machine
Perovskite Online PL Tester
Perovskite Online Sheet Resistance Tester
Online Perovskite Film Thickness Tester
Perovskite Process Inspection Workstation
Portable EL Tester
Portable Thermal Imaging Tester
Solar Module Multi-Channel Testing System
PV Inverter Power Quality Tester
Drone EL Tester
IV Tester
IVEL Cell Sorting Machine
Study on Outdoor Performance Degradation of Perovskite Cells: Sunlight-Excited Outdoor Photoluminescence and Implied Open-Circuit Voltage iVOC Imaging Technique
Date : 9 September 2025Views : 2365
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have achieved laboratory efficiencies exceeding 26%, yet large-area module efficiency maintenance and outdoor long-term stability remain barriers to their application. This study developed an imaging technique based on sunlight-excited outdoor photoluminescence (PL) and implied open-circuit voltage (iVOC), achieving the first quantitative spatial mapping of iVOC for perovskite cells and modules. The high-precision imaging capability of the Millennial Perovskite Online PL Tester enables clear identification of electron defect distributions. By optimizing bandpass filters to enhance signal-to-noise ratio and employing a single BPF calibration method to overcome sample optical property limitations, it achieves iVOC imaging accuracy <5%. This provides a new tool for investigating outdoor performance degradation mechanisms in perovskite cells.
PL Signal Extraction
In outdoor PL imaging, the camera-detected signal Idet comprises ambient light Iamb and PL signal IPL, where Iamb≫IPL.
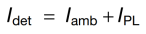
The study extracts effective PL signals by capturing PL images under open-circuit (OC) and short-circuit (SC) conditions:
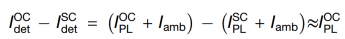
Principle: Under OC, Vi peaks → PL peaks; under SC, Vi≈0 → PL≈0, while the constant ambient light component Iamb cancels out.
Optical filter optimization
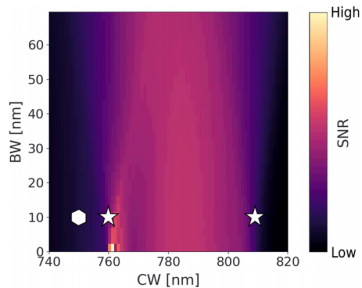
Optical Filter Optimization
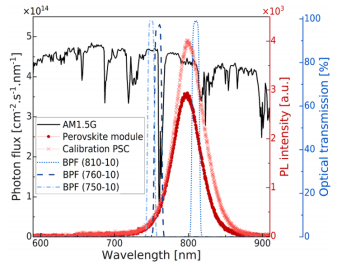
Optical Filter Selection
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is dominated by ambient light shot noise. Simulations indicate that for perovskite cells with a bandgap of 1.55 eV, a 10 nm bandwidth BPF centered at 760 nm maximizes SNR due to the absorption valley in the AM1.5G spectrum. Experiments using these parameters achieved PL image resolution approaching indoor levels.
Outdoor PL Imaging of Perovskite Microcells
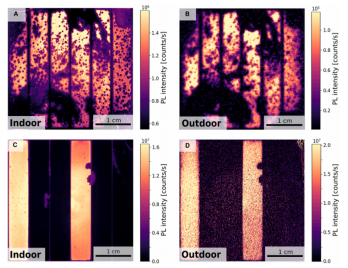
Outdoor PL imaging of perovskite micro-modules (A,C) versus indoor (B,D) PL images
Comparison of indoor/outdoor PL images:
Outdoor images successfully identified localized degradation zones (e.g., active layer defects, non-radiative recombination enhancement regions), showing high consistency with indoor results.
Resolution differences stem from lower outdoor SNR (limited by environmental light shot noise).
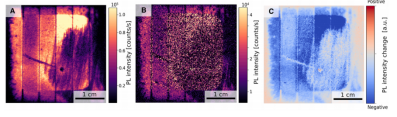
Perovskite Micro-Module Degradation Outdoor PL Imaging (A) PL image before aging, (B) PL image after 2 months of aging, (C) PL intensity decay curve
Two-month outdoor PL tracking of the same component:
Efficiency decreased from 10.3% to 1.7%, with significant PL intensity decay.
Spatial non-uniform decay: Localized regions exhibited more severe Vi decline, suggesting increased contact layer resistance or charge collection loss.
PL images correlate fill factor decay (via spatial distribution of shunt resistance) with short-circuit current loss (active layer degradation).
iVOC Imaging Method
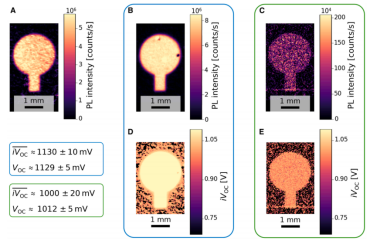
Outdoor iVOC imaging of PSCs: (A) PL image of reference PSC for calibration; (B, C) PL images of two PSCs under test; (D, E) corresponding iVOC images
Traditional calibration requires optical properties matching between samples and reference cells. This study employs a simplified single-BPF calibration method using a BPF with a 750 nm center wavelength and 10 nm bandwidth. It detects only the high-energy tail region of the PL spectrum—where PL intensity is insensitive to optical characteristics. This approach negates optical differences between calibration and test cells, controlling iVOC error within 5 mV.
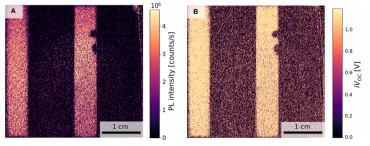
Outdoor iVoc Imaging of Perovskite Micro-Modules: (A) PL Image, (B) iVoc Image
For the first time, outdoor iVOC images of perovskite micro-modules were obtained. The module-level iVOC (3.5±0.5 V) aligns with the measured Voc (3.48±0.05 V).
This paper presents a novel method for capturing outdoor PL images of PSCs and perovskite modules using sunlight as the sole excitation source. This approach has been demonstrated to yield high-quality images revealing spatial information about PSC quality uniformity and the presence of various electronic defects, as validated by PL images obtained using an indoor laboratory PL imaging system. Beyond qualitative PL insights, we demonstrate that a single BPF method can be employed to calibrate PL signals into iVOC images. These iVOC distributions correlate with overall device performance and provide spatially resolved information on varying defect severities.
Millennial Perovskite Online PL Tester

email:market@millennialsolar.com
Online PL defect detection systematically addresses core challenges in solar cell production—speed, yield, cost, process optimization, and stability—through non-contact, high-precision, real-time feedback. Combined with AI deep learning, it enables fully automated defect identification and process feedback.
High-Precision PL Imaging: Utilizes line-scan laser with imaging accuracy <50μm/pixel (customizable)
High-Speed Online PL Defect Detection: Detection speed ≤2s, miss rate <0.1%; misclassification rate <0.3%
AI Defect Classification Training: Enables fully automated defect recognition and process feedback
Millennial perovskite online PL tester leverages high-precision PL imaging, high-speed inline detection, and AI defect recognition to enable rapid defect identification and process feedback during production. This not only provides comprehensive data support for optimizing perovskite cell performance but also accelerates its industrialization process.
































































