
Quantum Efficiency Tester
PL/EL Integrated System
PV-Reflectumeter
3D Confocal Microscope
In-Line Four Point Probe Tester
Four Point Probe Tester
In-Line Thin Film Thickness Tester
Raman Spectrometer
FTIR Spectrometer
Spectrophotometer
Automatic Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
Contact Resistance Tester
Ultra depth of field 3D microscope
Auto Visual Tester
VMM PV Vision Measuring Machine
Solar Cell Horizontal Tensile Tester
Steady State Solar Simulator for Solar Cell
Solar Cell UV Aging Test Chamber
Solar Cell Comprehensive Tensile Tester
Visual Inspection Tester
Wet Leakage Current Tester
PV Module EL Tester
PV Module UV Preconditioning Chamber
Steady State Solar Simulator for PV Module
Current Continuous Monitor
Potential Induced Degradation Test
Bypass Diode Tester
LeTID Test System
Reverse Current Overload Tester
Impulse Voltage Tester
Hipot Insulation Tester
Ground Continuity Tester
Hipot Insulation Ground Tester
Damp Heat Test Chamber
Humidity Freeze Test
Thermal Cycle Test Chamber
Dynamic Mechanical Load Tester
Static Mechanical Load Tester
Hail Impact Tester
Robustness of Termination Tester
Module Breakage Tester
Cut Susceptibility Tester
Peel Shear Strength Tester
Universal Testing Machine (Single-arm)
Universal Testing Machine (Double-arm)
Glass Transmittance Tester
Acetic Acid Test Chamber
EVA Degree of Crosslinking Test System
Junction Box Comprehensive Tester
Drop ball tester
Semi-automatic scanning four-probe tester
Stylus Profilometer
Maximum Power Point Tracker
Perovskite Glass Transmittance Tester
Perovskite P1 Laser Scribing Multifunctional Testing Machine
Perovskite Online PL Tester
Perovskite Online Sheet Resistance Tester
Online Perovskite Film Thickness Tester
Perovskite Process Inspection Workstation
Portable EL Tester
Portable Thermal Imaging Tester
Solar Module Multi-Channel Testing System
PV Inverter Power Quality Tester
Drone EL Tester
IV Tester
IVEL Cell Sorting Machine
Troubleshooting Air Bubbles in Laminated Solar panels
Date : 14 November 2025Views : 665
Air bubbles appearing in laminated Solar panels may result from multiple factors including raw materials, equipment, process parameters, environmental conditions, and operator practices. Below are specific cause analyses and solutions.
I. Material Anomalies
 Positioning Tape Bubbles
Positioning Tape Bubbles
① Positioning Tape Bubbles: Bubbles in positioning tape after lamination typically result from mismatched lamination parameters (primarily temperature and pressure) with the tape. This can be resolved by adjusting lamination parameters or replacing the positioning tape. (The author recommends replacing the tape, as adjusting temperature and pressure usually requires subsequent crosslinking degree and tensile strength testing, which is cumbersome.)
② Film Anomalies: Film bubbles usually stem from “dead material” within the film, localized adhesive deficiency, or low basis weight. “Dead material” bubbles are typically small and contain a white dot matching the film's raw material color.
Bubbles from localized film defects often reveal the embossed pattern from the glass substrate. When appearing on the front side of the cell, the cell may exhibit its natural blue color instead of black. Material defects can be resolved by replacing the material. If the cause cannot be definitively attributed to the material, cross-verification through material replacement can help identify the problematic material.
II. Equipment Abnormalities

Localized Temperature Anomaly Electrical Bubble
① Air Leakage: After the laminator closes its lid, air leakage may occur, leading to bubbles. The cause of bubble formation is localized air leakage around the chamber during vacuum extraction. Air enters the chamber through these leaks, resulting in insufficient vacuum pressure at those points and preventing bubbles from being fully extracted from the module. (Leaks vary in severity. Minor leaks typically produce bubbles along the module edges, especially on the short sides or corresponding long sides aligned with the laminator's head/tail positions. Major leaks trigger vacuum failure alerts, preventing proper vacuuming.)
To address air leaks, inspect the laminator's sealing rings, vacuum pump, vacuum lines, and other components. Also verify that the cover is fully closed and no foreign objects are obstructing the sealing ring or upper chamber flange after closure.
② Temperature: When lamination parameters are correct but non-snowflake-pattern bubbles appear on the front side (the side closest to the substrate during lamination) at a fixed position on a stationary laminator, consider whether localized overheating at the laminator's heating bottom causes premature cross-linking of the adhesive film at that spot. Use a spot thermometer to check temperatures and implement localized temperature compensation to resolve the issue.
Bubbles caused by localized temperature anomalies appear smoother compared to snowflake-pattern bubbles. They typically manifest as multiple small, relatively dense bubbles in a fixed position on the laminator at a fixed location.
III. Personnel Operations

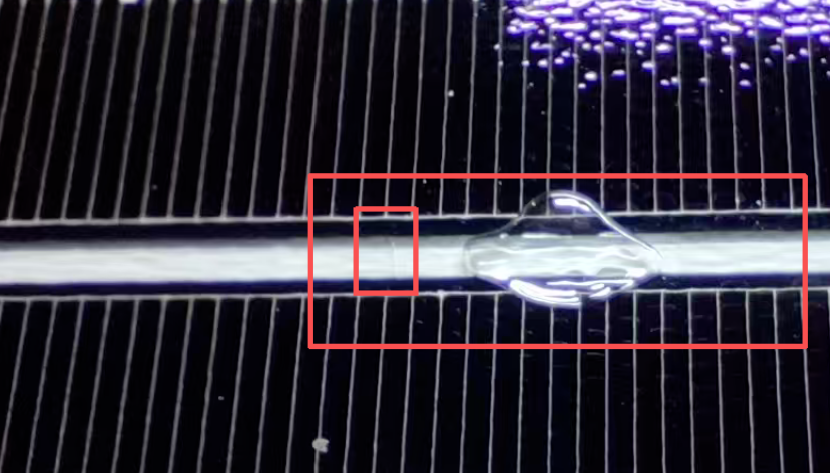
Bubbles formed when water splashes onto the plastic film
① Improper Film Application: During film placement, incorrect parameter settings by operators may result in insufficient film coverage, misaligned film positioning, missing edge strips, or excessively narrow application. This causes adhesive deficiency at module edges, leading to bubbles after lamination. Pre-EL inspection can confirm whether film application is the cause.
② Water Spillage on Film/Glass: Occasionally, water spilled onto the film or glass during cleaning or other operations can cause bubbles after lamination.
These bubbles exhibit a distinct water-sprayed appearance, differing entirely from bubbles caused by air leaks, film placement errors, or temperature anomalies.
IV. Environmental Issues
① High moisture content in film: When stored for extended periods in high-humidity environments, the film absorbs moisture. This leads to bubbles during lamination, appearing as small, randomly distributed air pockets.
③ Foreign object bubbles: Bubbles caused by foreign objects like insects result from substandard workshop conditions. This can be addressed by ensuring workshop personnel close doors promptly and implementing insect prevention measures.
































































