
Quantum Efficiency Tester
PL/EL Integrated System
PV-Reflectumeter
3D Confocal Microscope
In-Line Four Point Probe Tester
Four Point Probe Tester
In-Line Thin Film Thickness Tester
Raman Spectrometer
FTIR Spectrometer
Spectrophotometer
Automatic Spectroscopic Ellipsometer
Contact Resistance Tester
Ultra depth of field 3D microscope
Auto Visual Tester
VMM PV Vision Measuring Machine
Solar Cell Horizontal Tensile Tester
Steady State Solar Simulator for Solar Cell
Solar Cell UV Aging Test Chamber
Solar Cell Comprehensive Tensile Tester
Visual Inspection Tester
Wet Leakage Current Tester
PV Module EL Tester
PV Module UV Preconditioning Chamber
Steady State Solar Simulator for PV Module
Current Continuous Monitor
Potential Induced Degradation Test
Bypass Diode Tester
LeTID Test System
Reverse Current Overload Tester
Impulse Voltage Tester
Hipot Insulation Tester
Ground Continuity Tester
Hipot Insulation Ground Tester
Damp Heat Test Chamber
Humidity Freeze Test
Thermal Cycle Test Chamber
Dynamic Mechanical Load Tester
Static Mechanical Load Tester
Hail Impact Tester
Robustness of Termination Tester
Module Breakage Tester
Cut Susceptibility Tester
Peel Shear Strength Tester
Universal Testing Machine (Single-arm)
Universal Testing Machine (Double-arm)
Glass Transmittance Tester
Acetic Acid Test Chamber
EVA Degree of Crosslinking Test System
Junction Box Comprehensive Tester
Drop ball tester
Semi-automatic scanning four-probe tester
Stylus Profilometer
Maximum Power Point Tracker
Perovskite Glass Transmittance Tester
Perovskite P1 Laser Scribing Multifunctional Testing Machine
Perovskite Online PL Tester
Perovskite Online Sheet Resistance Tester
Online Perovskite Film Thickness Tester
Perovskite Process Inspection Workstation
Portable EL Tester
Portable Thermal Imaging Tester
Solar Module Multi-Channel Testing System
PV Inverter Power Quality Tester
Drone EL Tester
IV Tester
IVEL Cell Sorting Machine
TOPCon Cell Acetic Acid Fumigation-EL Testing | Rapid Prediction Method for Module Damp-Heat Test Results
Date : 17 November 2025Views : 735
TOPCon solar cell technology is advancing rapidly, yet it faces new reliability challenges stemming from wafer thinning, reduced silver consumption, and the widespread adoption of double-glass structures. While the 1000-hour damp-heat (DH) test per IEC 61215 is critical, its excessive duration fails to meet the demands for rapid process optimization in mass production. This paper proposes an accelerated acetic acid fumigation (AaF) test method at the cell level. By directly controlling acetic acid vapor concentration and temperature, this method bypasses the EVA hydrolysis process. Combined with the visual characterization of metal grid corrosion failure via electroluminescence (EL) testing using the Millennial PL/EL integrated tester, this approach efficiently replicates and quantifies the core failure mechanisms of DH at the cell level.
Experimental Design
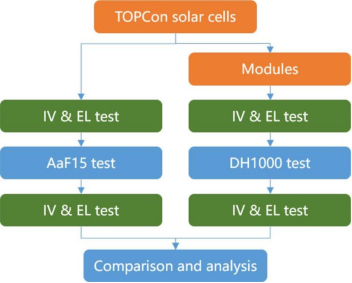
Experimental Roadmap
DH degradation primarily results from acetic acid corrosion of the battery's metal grid lines (emitter-silver paste interface) caused by hydrolysis of EVA encapsulation, leading to increased contact resistance (evidenced by darkened grid line edges in EL images). This paper proposes an innovative approach: bypassing the EVA hydrolysis process, it directly introduces acetic acid vapor to simulate the corrosion pathway. The method validates consistency between battery-level corrosion and module-level DH failure modes (both exhibit FF and Isc decline).
Cross-verification: Batteries from the same batch were divided into the AaF15 group (50 cells) and the DH1000 module assembly group (300 cells) to compare efficiency decay rates and EL images;
Variable Control: Three experimental groups varied only the silver paste formulation (primary factor), while encapsulation materials (POE/EPE) served as secondary variables to validate universality;
Stability Testing: Corrosion rate error <10% (mean 16.05%) across 10 homogeneous AaF15 cell groups, confirming method reproducibility.
AaF15 Test Results for TOPCon Cells
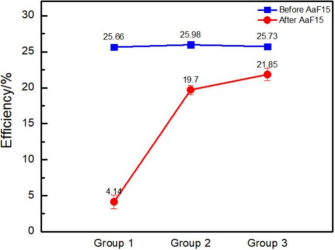
Efficiency Comparison of Three TOPCon Cell Groups Before and After AaF15 Testing
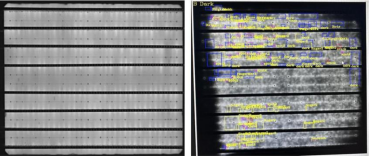
Comparison of Corrosion Features in EL Images of TOPCon Cells
AaF15 testing was conducted on three groups of TOPCon cells using different silver pastes. Significant efficiency degradation (varying in severity) and deterioration in electroluminescence (EL) images (edge darkening, blurred grid lines) were observed in all cases. This indicates that acetic acid successfully induced metal contact corrosion similar to dry etching (DH).
DH1000 Results for TOPCon Modules
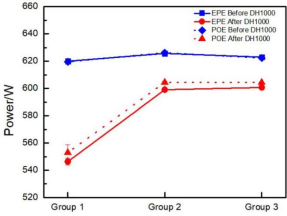
Comparison of DH1000 Degradation Rates Between POE and EPE Encapsulated Modules
Cells from the same batch as the AaF experiments were fabricated into solar modules. These modules underwent DH1000 testing. Each batch of TOPCon cells was divided into two groups, encapsulated using mainstream EPE and POE materials respectively. All DH-tested modules based on either EPE or POE exhibited varying degrees of degradation, consistent with the cell data.

Typical Failure Modes in EL Images of DH1000-Tested Components
EL images of components before and after DH testing reveal increased dark areas near the grid lines and main grid. This pattern aligns with the AaF results for the cells. Additionally, reduced lateral transport capability between the two metal grid lines has caused dark areas to appear in the grid line gaps.
Comparison of Acetic Acid Fumigation Testing with DH1000
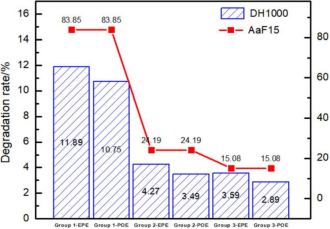
Linear mapping relationship between battery AaF15 degradation rate and module DH1000 degradation rate (R²=0.97)
The efficiency degradation rate of batteries after AaF15 shows a significant positive correlation with the power degradation rate of corresponding modules after DH1000. For example:
- Groups with battery degradation >80% exhibited module degradation >10% (far exceeding the 5% control line); For battery groups with ~24% degradation, the module degradation was ~4% (close to the control line); For battery groups with ~15% degradation, the module degradation was <3.6% (better than the control line).
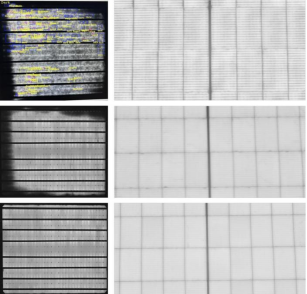
EL Comparison (After AaF15 Battery Treatment vs. After DH1000 Module Treatment vs. Original State)
Compare EL images showing severe degradation, mild degradation, and pre-degradation conditions. The EL degradation observed after AaF15 battery treatment aligns with that after DH1000 module treatment, further validating the predictive methodology.
Stability Verification
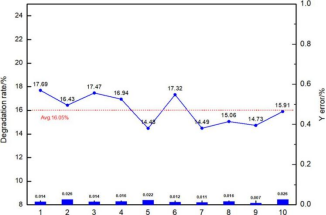
Stability Validation of AaF15 Testing for Batch-Matching Batteries
Ten sets of AaF15 tests conducted on batch-matched batteries yielded an average degradation rate of 16.05%, with a fluctuation range of 14.48%–17.69% (maximum error <10%). This demonstrates sufficient stability for mass production monitoring.
The AaF15 accelerated test results for TOPCon cells show significant correlation with module DH1000 outcomes, enabling effective prediction of module DH failure risks. Experimental and error analysis indicate that to ensure module DH1000 degradation ≤5%, cell AaF15 degradation should be controlled below 24%. Practical application recommends adopting a stricter 20% threshold. Requiring only 15 hours, this method provides a rapid, stable, and efficient reliability monitoring tool for TOPCon cell mass production (e.g., silver paste selection, process optimization), significantly reducing mass production risks caused by DH failure.
Millennial PL/EL Combo Tester

email:market@millennialsolar.com
The Millennial PL/EL Integrated Tester simulates sunlight irradiation on perovskite solar cells, uniformly illuminating the entire sample. It captures photoluminescence (PL) signals using specialized lenses to generate PL images, and electroluminescence (EL) signals to produce EL images. Image algorithms and software process and analyze the captured PL/EL images, identifying PL/EL defects for subsequent analysis, classification, and summarization based on their characteristics.
EL/PL imaging, 5 megapixels, with multiple imaging precision modes
Spectral response range: 400nm–1200nm
PL light source: Blue light (customizable light source size, wavelength, etc.)
Multiple defect recognition and analysis (pitting, darkening, edge intrusion, etc.) with customizable defect types
The Millennial PL/EL Integrated Tester utilizes electroluminescence (EL) signals to generate EL images, enabling visual characterization of metal grid corrosion failure. It efficiently reproduces and quantifies the core mechanisms of DH failure at the cell level, providing a reliable monitoring tool for TOPCon cell mass production.
Related Products
































































